

Financial solvency plays a key role in financial planning and loan application evaluations. Learn how to measure and maintain it. We’ll look at what financial solvency is, how it differs from liquidity and why it’s important. Then we’ll review how to measure and evaluate solvency. Finally, we’ll suggest some strategies to improve your company’s solvency.
Financial solvency refers to a company’s ability to repay long-term debt obligations such as loans, mortgages and bonds. It is gauged by using one of several methods to compare a company’s assets to its liabilities. Long-term solvency reflects the ability of a company to sustain its operations indefinitely for the foreseeable future. This makes business solvency an important consideration for financial planning. Lenders and investors who are evaluating whether to extend financing to a company weigh in solvency risk when making decisions.

Liquidity refers to a company’s ability to obtain cash quickly to cover short-term expenses and debts. It considers a company’s ability to access cash and assets which can convert quickly into cash such as marketable securities. Liquidity has a shorter-term focus than solvency, and the two measures are not interchangeable. Liquidity focuses on current assets and liabilities, whereas solvency includes long-term assets and liabilities. Solvent companies generally have the ability to achieve liquidity rapidly by tapping into long-term assets. However just because a company has short-term liquidity doesn’t imply that it has the means to cover its long-term debts.
These factors make solvency a vital consideration for both companies and financing partners.
There are several formulas commonly used to measure company solvency. In general, they involve financial ratios comparing a company’s assets to its liabilities.
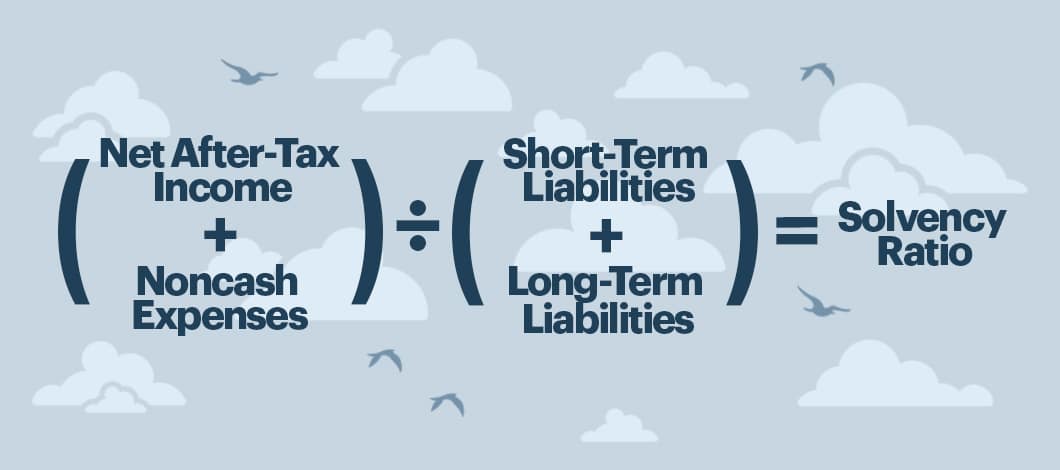
A standard solvency ratio uses the formula:
(Net after-tax income + noncash expenses) / (Short-term liabilities + Long-term liabilities)
This solvency ratio example is a common solvency formula, but others may be used.
Different solvency formulas include:
Which specific solvency ratio to use depends on what you need to evaluate. Your accounting professional can help you determine which ratio is most relevant to your current needs.
Related: A Comprehensive Guide to Measuring Your Small Business Liquidity RatioYou can obtain the data necessary to assess the solvency of your company or another company by looking at the company’s financial statements. The most important statement is the balance sheet. This provides a summary of all assets and liabilities, along with an itemized breakdown.
A company’s cash flow statement also provides insight into a company’s solvency. This can show if a company has a large amount of outstanding debt, how much is going toward repaying debt and how much resources are available to cover current and upcoming debt payments.
Companies that are struggling with solvency issues can pursue a number of strategies to improve solvency ratios by either increasing assets or reducing liabilities.
In general, any strategy which increases your assets or lowers your liabilities will tend to help your solvency ratio.
Financial solvency measures a company’s ability to repay long-term debt obligations such as loans. It differs from liquidity, which focuses on the ability to repay short-term obligations. Evaluating solvency is important for companies planning how to cover debt repayments and for lenders and investors assessing credit risks.
Solvency can be measured by using a variety of formulas that compare assets to liabilities. The most common formula compares net after-tax income minus noncash expenses to total liabilities. Different formulas focus on varying specifics, such as assets after inventory is factored out or the ability to meet interest payments. Which formula to use depends on the purpose of the solvency analysis. Information for calculating solvency formulas can be obtained from balance sheets.
Improve solvency by implementing financial management strategies that increase your assets, reduce your liabilities or both. Manage your solvency ratios to make sure you can cover your debt obligations and you’re in a position to qualify for financing when you need it.
If you’re seeking financing options, take a few minutes to fill out our free, no-obligation prequalifying form and see which loan options may be available to you today with your current financial numbers.

Roy is a respected, published author on topics including business coaching, small business management and business automation as well as an expert business plan writer and strategist.